Projects
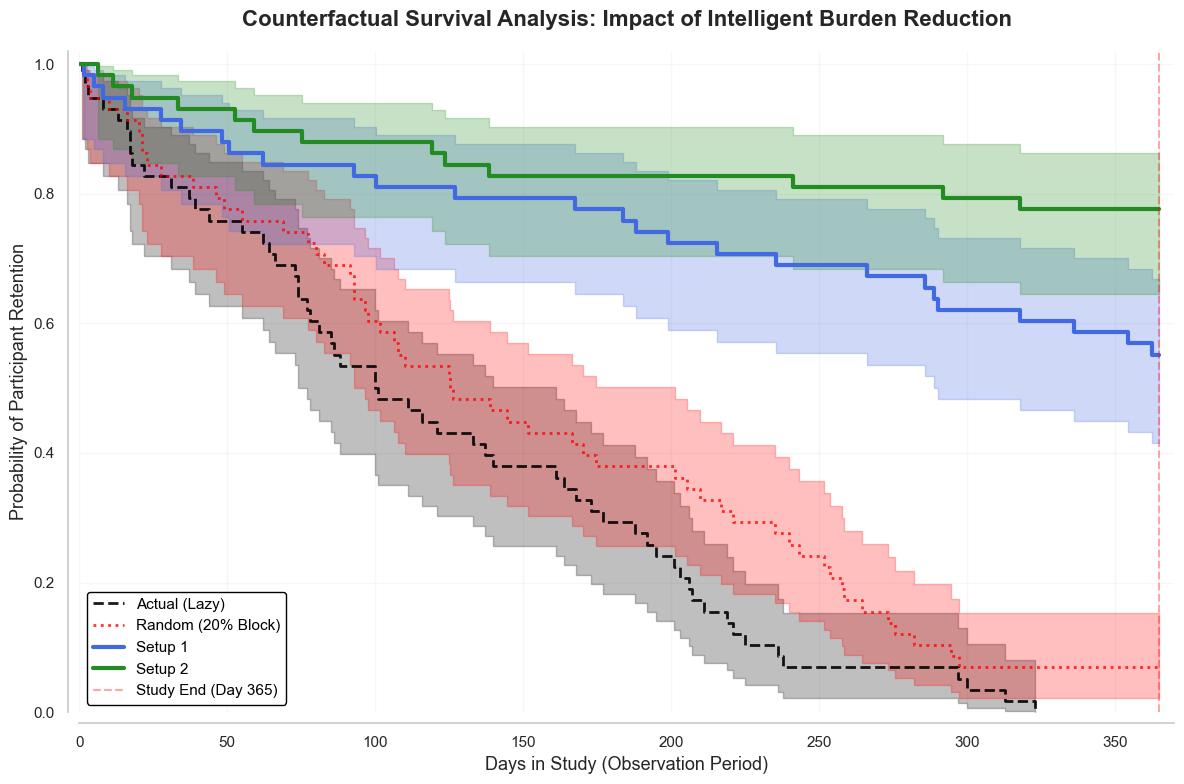
Context-aware model for experience sampling [WIP]
How can we reduce user burden in real-time experience sampling? Experience sampling becomes burdensome when users are prompted too frequently. Trained a neural network to predict moments when interruptions would be least disruptive, using users’ multimodal context, such as inertial sensor data. Compared two training strategies: depth (more data from fewer users) and breadth (less data from more users). Counterfactual analysis on real-world data showed that the breadth-based model outperformed both a random baseline and the depth-based model by over 40%, leading to higher long-term user engagement and lower user burden.
Personalized experience sampling surveys
How can we personalize survey question selection in real time? User behavior models rely on high-quality survey data, but frequent surveys increase user burden. Developed machine learning methods to personalize longitudinal survey collection, improving data quality while reducing burden. Conducted two large-scale studies: 1) used mixed-effects models to predict non-response bias in experience sampling surveys; 2) used Bayesian Networks to personalize survey question selection in real time, prioritizing questions with the highest expected information gain (i.e., greatest reduction in uncertainty).
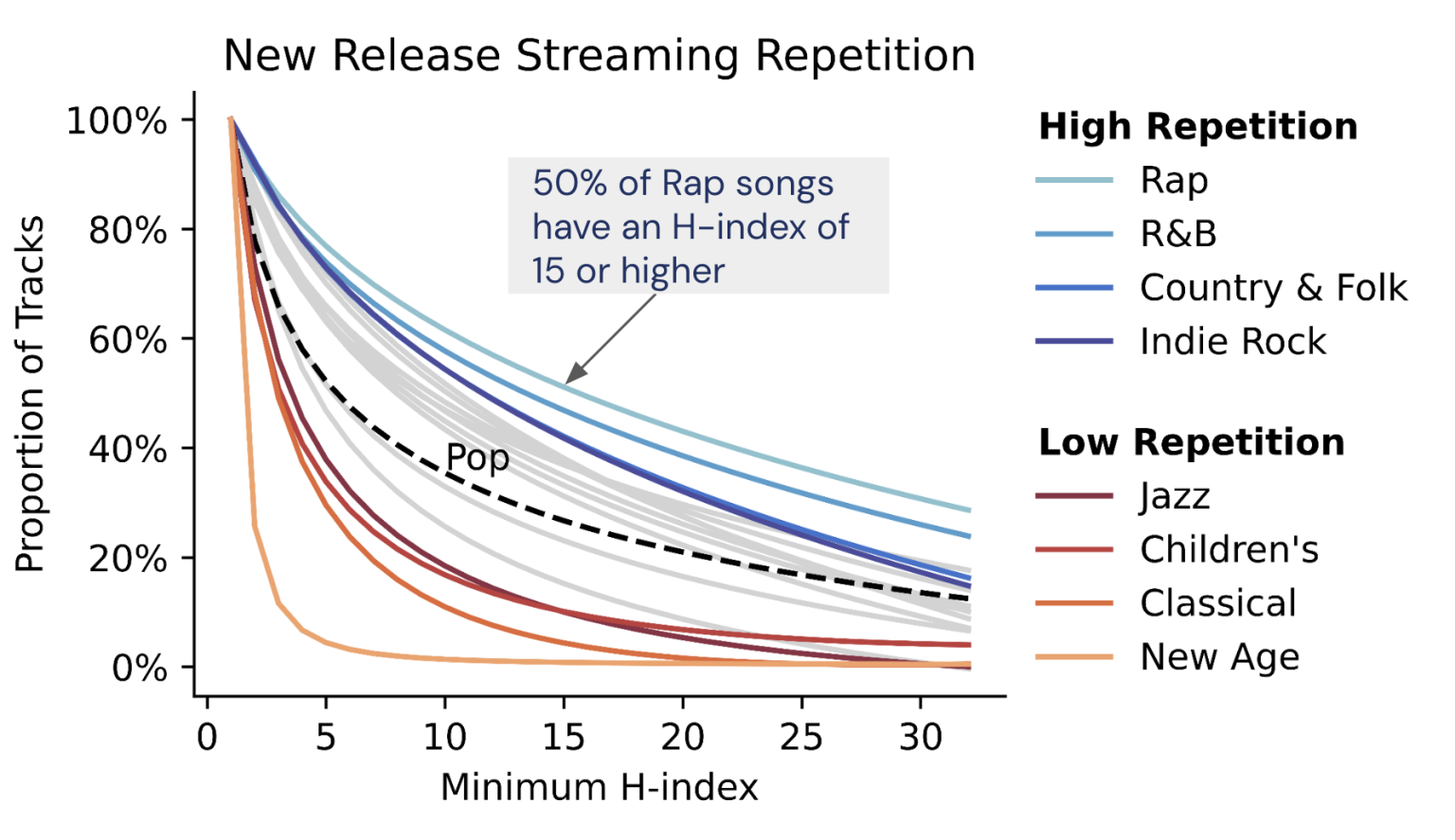
User modeling of new music listening
How do users discover and stream new music? Built machine learning models to predict how users interact with new music recommendations, including genre success forecasting, taste classification, and user segmentation. Findings showed that genre popularity strongly influences repeat listens, users have different tastes for new versus older music, many follow a stable “new music” listening pattern, and some user segments are more receptive to new recommendations. These insights informed A/B tests on Spotify Home, leading to about a 14% increase in new music discovery. Read more
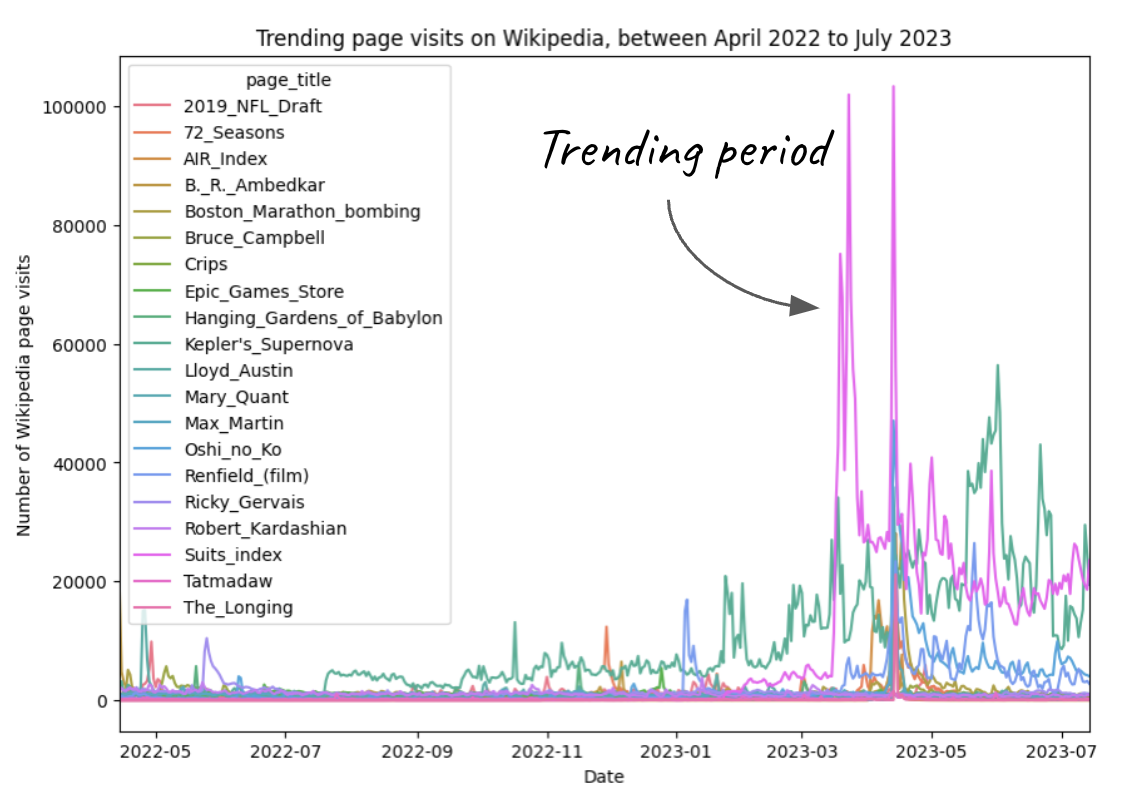
AI-enabled podcast content understanding
How can smaller podcasters grow their audience? Developed an LLM-enabled approach to help long-tail podcasters benefit from emerging trends. First, created an algorithm to detect trending topics using Spotify search queries and Wikipedia page views. Second, evaluated top-K search results from trending queries for long-tail content share. Third, built an AI-based system that matches these trends to relevant long-tail podcasts. Showed that LLM text embeddings outperform zero-shot prompting in speed and accuracy when matching topics to podcast episodes. Observational analysis confirmed that surfacing trending topics increased podcaster growth and user engagement.
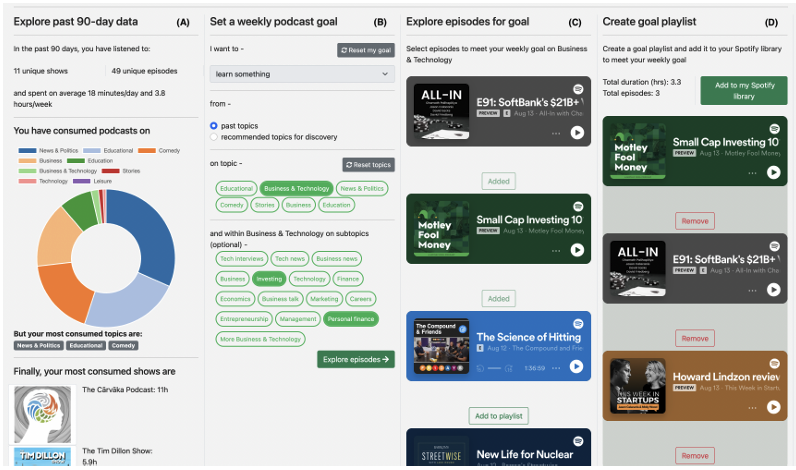
Podcast discovery via goal-setting
How does user input improve discovery? Built an interactive AI prototype (inspired by Strava/Duolingo) where users set goals to receive personalized podcast recommendations. Used large-scale event-triggered surveys and search queries to identify user needs, revealing a gap between long-term goals (e.g., learning) and short-term entertainment needs. Real-world evaluation showed that goal-setting helped users discover new podcasts. Read more
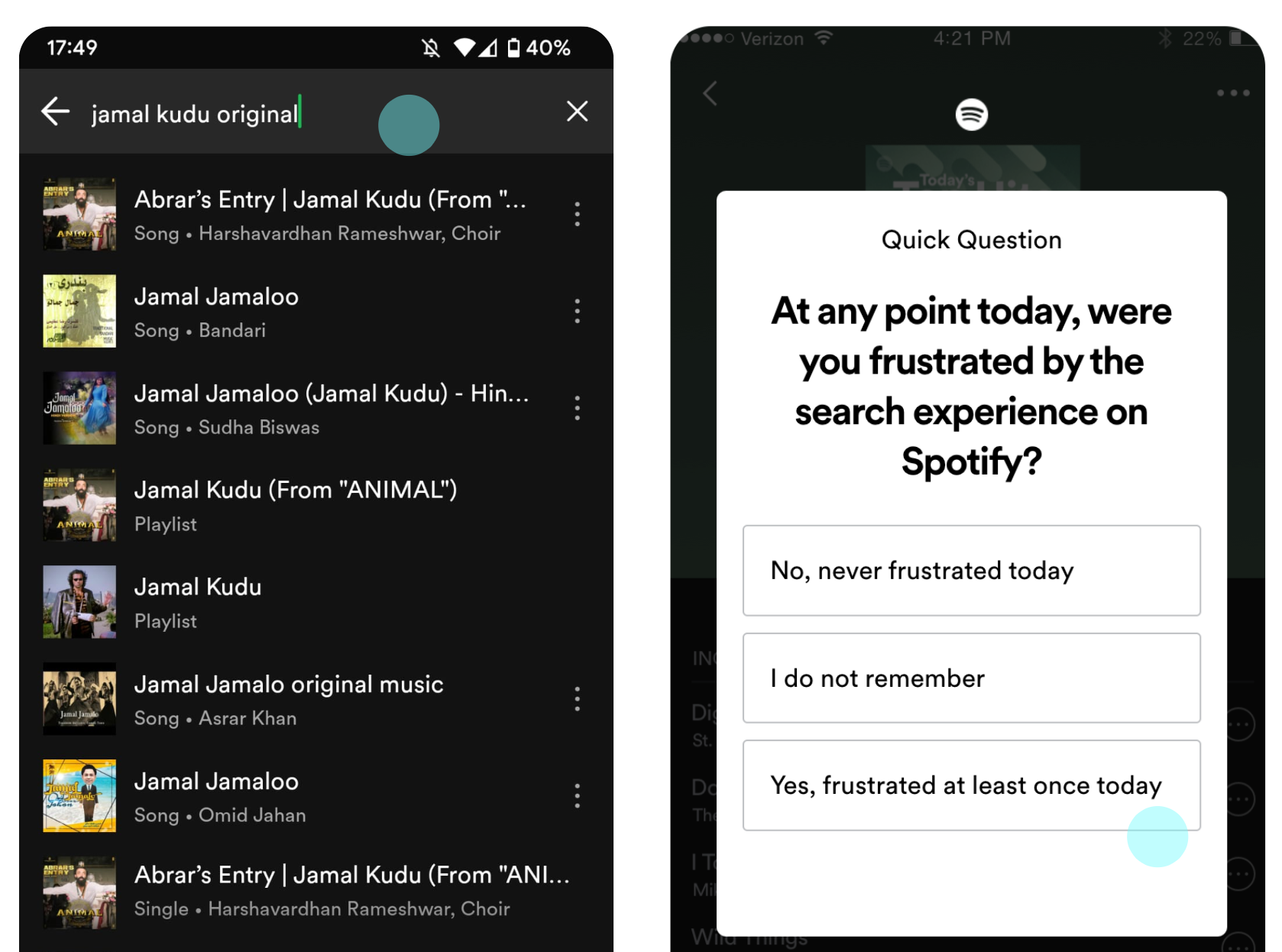
Measuring search user frustration
Can we predict user frustration with search? Developed a novel UX metric for Spotify search frustration by collecting large-scale session-level labels via event-triggered surveys. Built an ML model predicting frustration using search interactions, revealing two key insights: frustration is session-dependent rather than user-history-based, and query edit distance is the strongest predictor. These findings enabled real-time frustration measurement in online experiments to improve the search experience.

MicroEMA: Experience sampling via smartwatch microinteractions
How can we collect high-density training data without overburdening users? Designed a smartwatch-based experience sampling technique that presents surveys as lightweight, glanceable microinteractions—single-question with binary responses. This interaction design minimizes interruption and cognitive load. It aslso enables reliable, high-frequency labeling in naturalistic settings. In longitudinal field studies, this approach doubled response rates compared to traditional multi-question surveys while reducing user burden, making it effective for large-scale human data collection to train and evaluate pattern recognition models. Read more
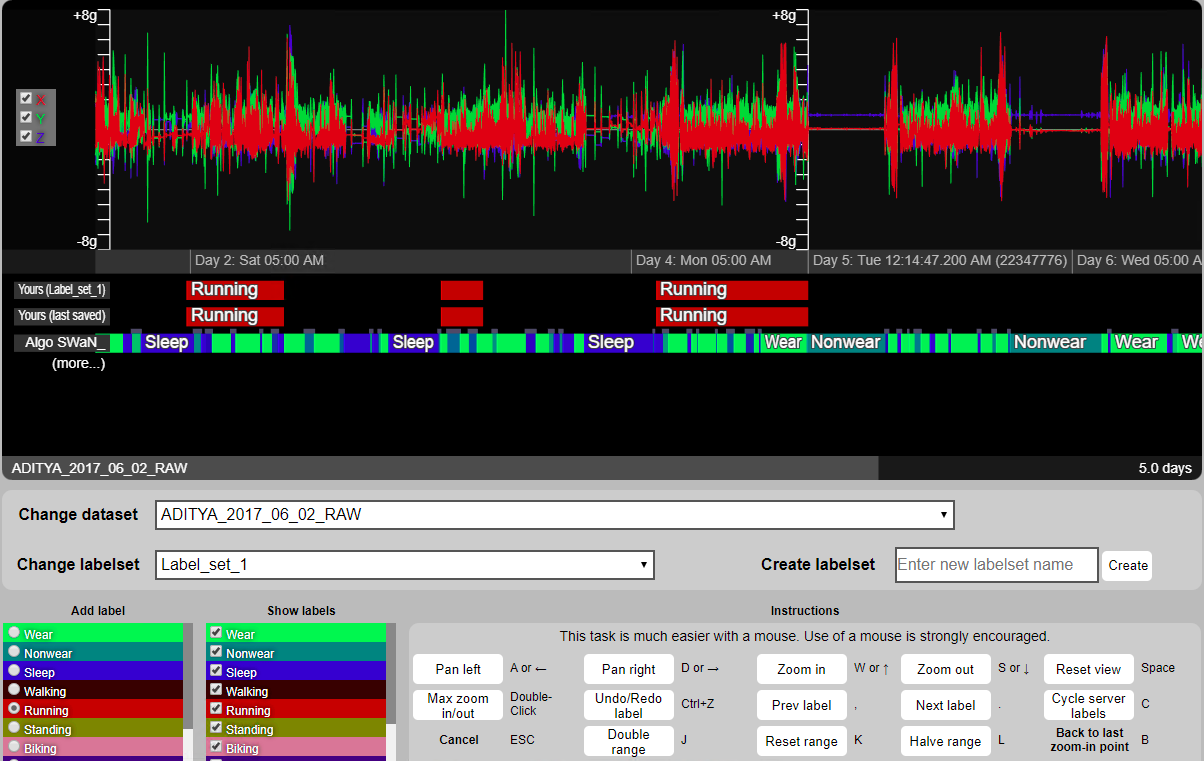
Signaligner Pro: AI-assisted sensor data labeling
How can we make data labeling scalable and reliable for ML? Built Signaligner Pro, an open-source, AI-assisted tool for labeling wearable sensor data at scale. The system supports efficient annotation of activities such as walking and running by combining human-in-the-loop precision with automated model suggestions. Signaligner Pro is now used in multiple NIH-funded studies, for high-quality label generation and supporting the development of more robust and generalizable ML models through human–AI collaboration. Try it here
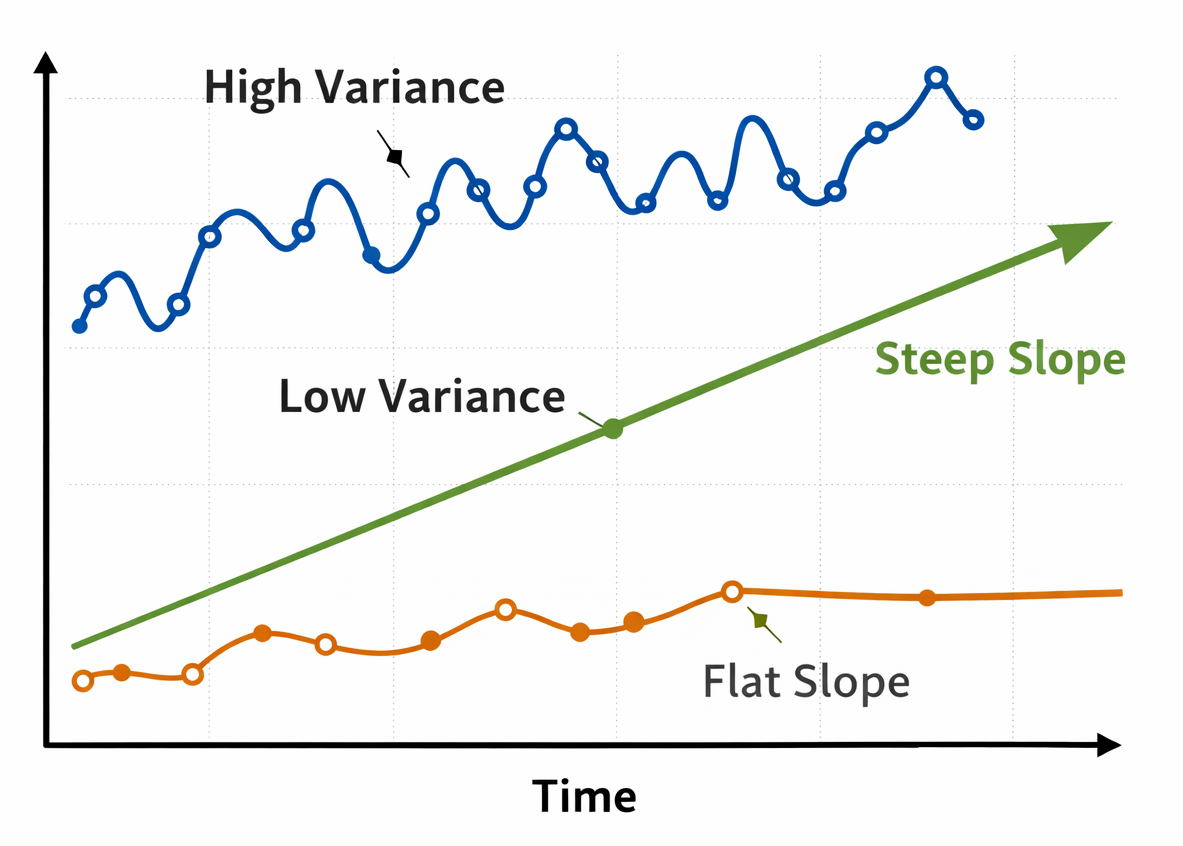
MixWILD: Interactive mixed-effects modeling
What if we could build statistical models without coding? MixWILD is an open-source modeling tool for intensive longitudinal data that estimates individual differences in both mean levels and variability of time-varying processes (like change in stress levels), including random slopes. It uses mixed-effects location-scale models and second-stage analyses to examine how within-person variability and change relate to predictors and outcomes. Try it here
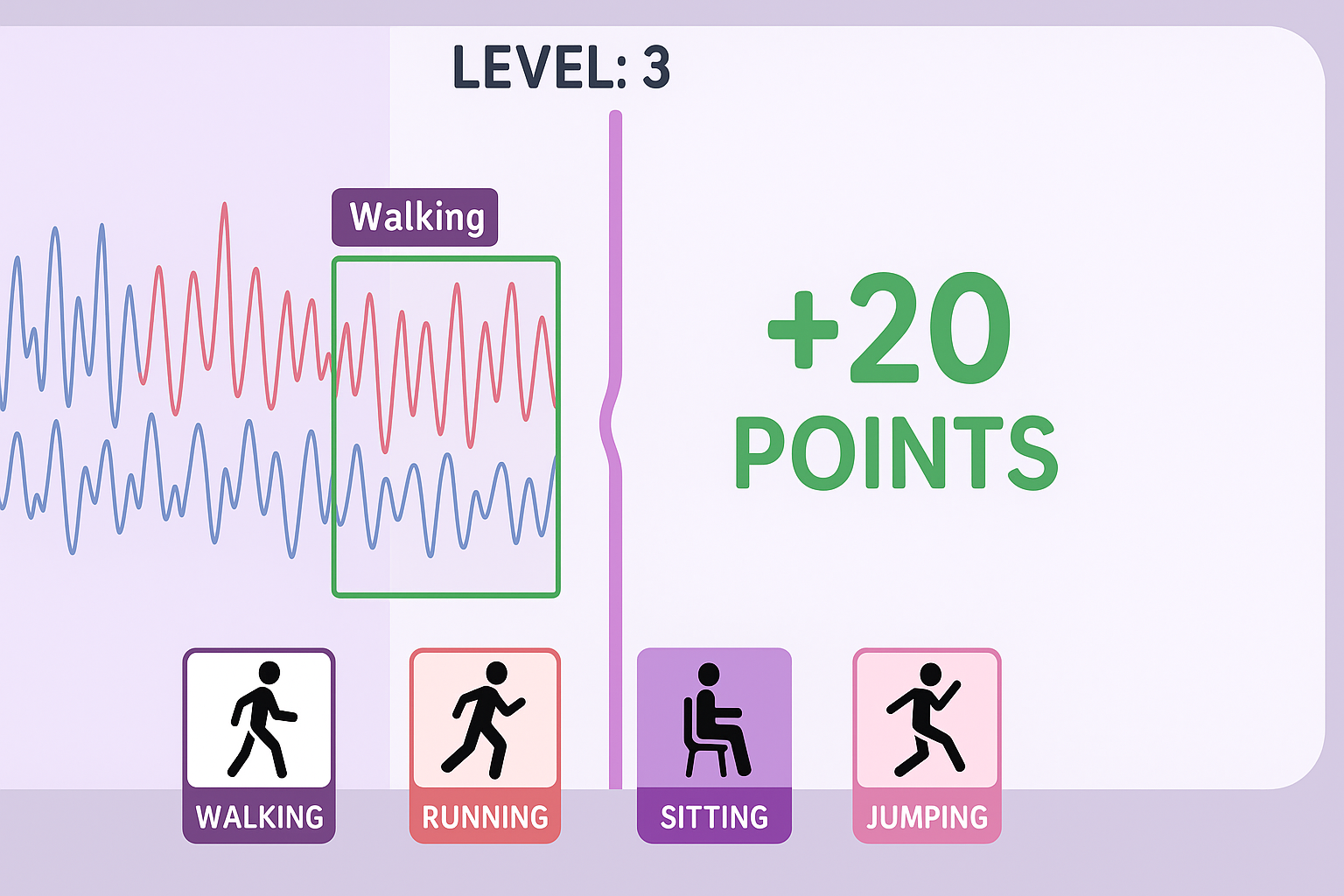
Video games for human data labeling
Can video games help train AI? Designed video games to crowdsource labeling of sensor data for activity-recognition models, turning tedious manual annotation into engaging gameplay. Experiments showed that casual players without AI expertise could produce high-quality labels, and that puzzle-based games led to higher label accuracy and engagement than endless runner-style games. VentureBeat converage)
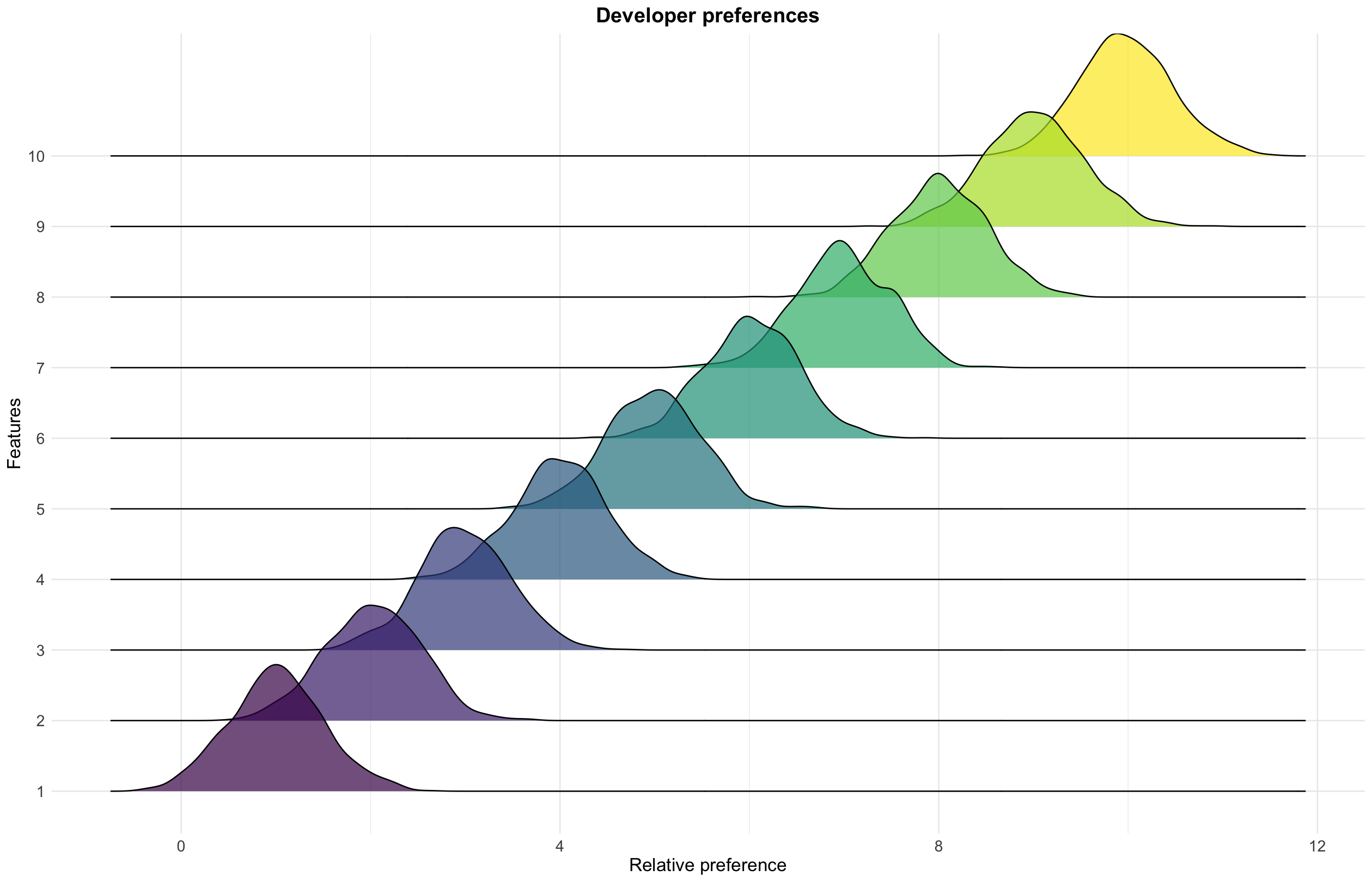
Modeling developer preferences
What do developers care about most? We used discrete choice models to study developer preferences for MongoDB Atlas through large-scale MaxDiff surveys. The surveys captured trade-offs between cost and performance, revealing clear differences between novice and experienced developers. These insights informed A/B experiments for personalized developer experiences, leading to > 8% improvement in user engagement and task success.
UX metrics for developer experiences
How do we measure the success of design changes? We developed new UX metrics to evaluate the MongoDB Atlas experience at scale, including measures of developer sentiment, engagement, and task success. These metrics were used to assess design changes across observability, identity and access management, and billing interfaces, providing a scalable, data-driven framework for cross-functional teams.
